Electricity:
Electricity deals with the motion of the electric charge.Electric charge is a scalar quantity which unit is Coulomb.Electricity produced by the friction between two bodies is called static electricity or frictional electricitye.g. generation of electric charge on rubbing the plastic comb with dry hair.
Coulomb Law:
The magnitude of the electrostatic force of interaction between two charge points is directly proportional to the scalar multiplication of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Electric Field:
The space in the surrounding of any charge in which its influence can be experienced by other charge is called electric field.Electric field intensity (E) at any point is defined as the electrostatic force acting per unit positive test charge at that point. Its unit is Newton/coulomb.E=F/qElectric field intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance r from the point charge.
Electric Field Lines:
The electric field line is an imaginary lines or curve drawn through a region of space so that its tangent at any point is in the direction of the electric field vector at that point.Two lines an never intersect, electric field always start from the positive end and always ends on the negative charge and do not start or stop in the mid.
Electric potential:
The electric potential at any point in an electric field is equal to the work done per unit charge in carrying at least a test charge from infinity to that point. Its unit is joule/coulomb.The potential difference between two points in an electric field is equal to the work done per unit charge in carrying a positive test charge from one point to the other point.Potential difference decides the flow of charge between two points in the electric field.Positive charge always tends to move from higher potential towards lower potential.Inside the closed metallic body, the electric field is zero.
Electric current:
Electric current is the flow of charge with respect to time.Electric current=q/tAn electric current whose direction does not change with time is called direct current (D.C).An electric current whose direction changes with time is called alternating current (A.C).In solids- Current flow due to the flow of electrons
In the liquid- Current flow due to the flow of ions as well as electrons
In semiconductors- Current flow due to the flow of electrons and holes.
Resistance:
The resistance offered by any material in the flow of current is called as electrical resistance. Its S.I unit is ohm and [ML2T-3A-2] is its dimension.R=PL/AL=length of conductorA=cross sectional areaThe P= resistivity of the material.
Conductance
Conductance or conductivity is thereciprocal of resistance and the resistivity of the material respectively.Its SI unit is mho.
Resistivity
The resistivity of a material is equal to the electrical resistance of its wire unit length and of the unit area of cross-section.Its unit is ohm-meter.The resistivity of a material depends on the temperature and nature of the material.It is independent of dimensions of the conductor, i.e. length, area of cross-section.The resistivity of metals increases with increase in temperature.Resistivity is low for metals, more for semiconductors and very high for alloys.
Combination of Resistances
Resistance can be connected in two ways i.e. in parallel and in series.(a) Series
If resistance R1, R2 and R3 are connected in series their equivalent resistance is given by
R= R1+R2+R3
In series combination equal current flows through each resistor.(b) Parallel
If resistance R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel then equivalent resistance is given by.
1/R =1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3
Ohm’s Law
It states that if physical conditions of any conductor such as temperature, pressure etc. remain unchanged then electric current(I) through it is directly proportional to the potential difference(V) applied across its ends. V=IR
Kirchoff’s Law:
Kirchoff current law: states that the net current on a junction in an electrical circuit will be zero. It is based on conservation of charge.
Kirchoff’s Voltage Law- states that the algebraic sum of all potential difference along a closed loop is Zero. It is based on conservation of energy.
Electric Cell:
An electric cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.Electric cell is of two types:
(a) Primary cell: cannot be charged. Voltaic, Daniell and Leclanche cells are primary cells.
(b) Secondary Cell: can be charged again & again. Acid and alkali accumulators are secondary cells.
Joule’s Law of Heating
Joule heating describes the process where the energy of an electric current is converted into heat as it flows through a wire due to the resistance of the wire. Heat produced in the conductor due to electric current in time “t” is given byH=VIT=I2RT=V2t/rElectric bulb and heater work on the basis of the heating effect produced by the current.
Chemical Effect of Electric current:
When an electric current is passed through an acidic or basic solution, it decomposes into its positive and negative ions. The positive ions collect at the negative electrode(Cathode) and the negative ion is collected at the positive electrode (anode).This phenomenon is called electrolysis.
Faraday’s Law of Electrolysis
First law:
The total mass (M) deposited at an electrode in the process of electrolysis is directly proportional to the total charge (q) passed through the electrolyte.M=Zq, where Z is the electrochemical equivalent of the substance deposited at the electrode.
Second law:
If the same strength of the electric current is allowed to pass through different electrolytes for the same time, then mass deposited at the electrodes is directly proportional to their chemical equivalent.M1/M2 =E1/E2
Electric Power
P = V2/R = I2R
Here P= Electric Power, V= Voltage, R= Resistance
Electric Fuse
Used to preotect electric appliances from high current.Fuse wire made of the alloy of copper, tin and lead.The material of fuse wire should be low melting point and high resistance.
Shunt
It is the wire of very small resistance.If we add shunt parallel to galvanometer, then galvanometer act like an ammeter.
Note-
If we add high resistance in series with the galvanometer, then galvanometer act like a voltmeter.
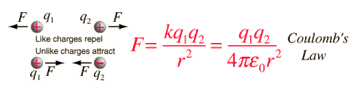
Good stuffs
ReplyDelete